
Li Min, Professor, master/doctoral supervisor, candidate of Hubei Talent Program, CUG scholar – Young Talents Program, IEEE Member. She was born in July 1990, received the B.E. degree from Huazhong University of Science and Technology in 2012, the PhD degree in Engineering from Tsinghua University in 2017, and was named Professor of China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) in 2021. She has presided over one general program and one youth program of National Natural Science Foundation of China and one youth program of Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province, and 4 other provincial and ministerial level/enterprise sponsored research projects, with a total research funding of over RMB 2 million. She has participated in 02 Subject of National Science and Technology Major Project, including “development and integration of double-scan silicon table mask prototype for photolithography”, and “research on the key technologies for magnetically levitated workbench”. She has published more than 20 academic papers, including 10 first-author papers in top international journals such as IEEE T-II and IEEE T-IE, with 164 SCI citations and the highest single SCI citation of 34, and has been granted 4 invention patents. The research results have been successfully applied to the 65nm lithography machine developed independently in China. She has been invited to give one presentation at international conference and served as the program committee chair for three times; and she also serves as a reviewer for IEEE T-MECH, MSSP and other journals.
Contact Information
E-mail: minli@cug.edu.cn
Address: Room 339 (No. 2 Teaching Building), School of Mechanical Engineering and Electronic Information, China University of Geosciences
Main Experiences:
2021/06-present: Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering and Electronic Information, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan)
2017/07-2021/05: Associate professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering and Electronic Information, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan)
2012/09-2017/06: Doctor of Engineering in Mechanical Engineering, Tsinghua University
2008/09-2012/06: Bachelor of Engineering in Mechanical Design, Manufacturing and Automation, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Research Fields:
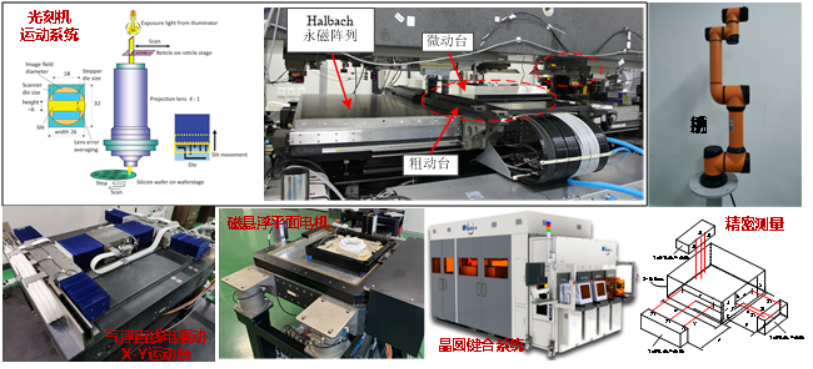
[1] Precision/ultra-precision dynamics modeling: It focuses on precision/ultraprecision motion systems in integrated circuit manufacturing equipment, CNC machine tools, robots, etc., reveals the "force-electricity-magnetic" multi-physical field coupling and rigid-flexible coupling mechanism, and studies the parametric dynamics modeling methods.
[2] Machine vision and precision measurement: In order to meet the measurement, positioning and recognition requirements of micro/nano precision for precision machining and measuring equipment, it studies new high-precision, multi-dimensional measurement technologies and their applications in engineering based on machine vision, laser interference and other technologies.
[3] Precision/ultra-precision motion control: Based on the data driven control theory, it studies the decoupling control, feedback control, feedforward control and disturbance suppression methods for the performance index requirements complex dynamic characteristics and multi-source disturbances of precision/ultra-precision motion systems approaching physical limits.
[4] Micro-nano-manipulated robots: Based on intelligent materials and micro/nano scale dynamics, characterization and control technologies, micro/nano manipulated robots driven by electromagnetic, electrostatic, electrothermal, piezoelectric, and photoelectric methods are studied.
Admission Requirements:
We welcome the master and doctoral students from mechanical, control, computer, measurement and control, and electrical and electric related majors, who love scientific research, are interested in machine vision, advanced control and precision electro-mechanical system, and have good programming and practical skills, to join the research group. Both master and doctoral candidates are admitted. Our graduate students have the opportunity to study and exercise in Tsinghua University and Beijing U-precision Tech Co., Ltd.
Scientific Research Programs:
[1] General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China: Multi-field rigid-flexible coupling modeling and modal decoupling control of flexible magnetic levitation planar motors (52275072), 2023/01-2026/12, RMB 540,000 Yuan, PI.
[2] Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China: Research on Multivariable Control of Large Stroke Ultra-Precision Workbench Based on Data Driven (51805496), 2019/01-2021/12, RMB 270,000Yuan, PI.
[3] Youth Program of Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province: Data-driven multivariable control of ultra-precision motion tables for photolithography (2019CFB206), 2019/01-2020/12, RMB 50,000Yuan, PI
[4] University cooperation project: Data-Driven Nonlinear Control Technology and Development of Its Application System, 2018/08-2022/12, RMB 1,000,000Yuan, PI.
[5] Enterprise sponsored program: Development of three-coordinate scanning experimental platform, 2020/11-2021/11, RMB 140,000Yuan, PI
[6] Program supported by Space Science and Technology Foundation, Research on the integrated guidance and control of hypersonic vehicle based on the dynamic linear model free adaptive control, 2018/06-2019/06, RMB 80,000Yuan, PI.
[7] Program supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities: Study on the Motion Control of Ultra-Precision Workbench of Lithographic Machine (CUG170667), 2017/07-2020/07, RMB 350,000Yuan, PI.
[8] 02 Subject of National Science and Technology Major Project: Development and integration of double-scan silicon table mask prototype for photolithography (2009ZX02208-001), 2012/09-2016/04, participant.
[9] 02 Subject of National Science and Technology Major Project: Research on the key technologies for magnetically levitated workbench (2012ZX02702-006), 2012.09-2017.07, participant.
[1] M. Li, J. Xiong, R. Cheng, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, and F. Sun. Rational Feedforward Tuning Using Variance-Optimal Instrumental Variables Method Based on Dual-Loop Iterative Learning Control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, Early Access, DOI: 10.1109/TII.2022.3166590. (Q1, IF: 11.65)
[2] M. Li, T. Chen, R. Cheng, K. Yang, Y. Zhu, and C. Mao. Dual-Loop Iterative Learning Control With Application to an Ultraprecision Wafer Stage. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(11): 11590-11599. (Q1, IF: 8.16)
[3] M. Li, C. Mao, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, and X. Li. Data-Based Iterative Dynamic Decoupling Control for Precision MIMO Motion Systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(3): 1668-1676. (Q1, IF: 11.65)
[4] M. Li, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, L. Yang, and C. Hu. Data-Based Switching Feedforward Control for Repeating and Varying Tasks: With Application to an Ultraprecision Wafer Stage. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(11): 8670-8680. (Q1, IF: 8.16)
[5] M. Li, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, L. Yang, C. Hu, and H. Mu. Convergence Rate Oriented Iterative Feedback Tuning with Application to an Ultraprecision Wafer Stage. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(3): 1993-2003. (Q1, IF: 8.16)
[6] M. Li, K. Yang, Y. Zhu, H. Mu, and C. Hu. State/Model-Free Variable-Gain Discrete Sliding Mode Control for an Ultraprecision Wafer Stage. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(8): 6695-6705. (Q1, IF: 8.16)
[7] M. Li, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, C. Hu, and H. Mu. An Integrated Model-Data-Based Zero-Phase Error Tracking Feedforward Control Strategy with Application to an Ultraprecision Wafer Stage. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(5): 4139-4149. (Q1, IF: 8.16)
[8] M. Li, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, and C. Hu. A Data-Driven Variable-Gain Control Strategy for an Ultra-Precision Wafer Stage with Accelerated Iterative Parameter Tuning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2015, 11(5):1179-1189. (Q1, IF: 11.65)
[9] M. Li, C. Mao, M.-F. Ge, and J. Gan. Data-Driven Iterative Feedforward Control with Rational Parametrization: Achieving Optimality for Varying Tasks. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 365(12): 6352-6372. (Q2, IF: 4.25)
[10] M. Li, T. Yan, C. Mao, L. Wen, X. Zhang, and T. Huang. Performance-enhanced iterative learning control using a model-free disturbance observer. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2021, DOI: 10.1049/cth2.12096. (Q3, IF: 2.67)
[11] M. Li, S. Tan, J. Xiong, J. Gan, and X. Zhang. Model-free output feedback discrete sliding mode control with disturbance compensation for precision motion systems. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2020, 14(14), 1867-1876. (Q3, IF: 2.67)
[12] M. Li. Data-Driven Control for Precision Motion Stages, Keynote Speaker, 2019 3rd IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Sciences, Wuhan, 2019/06/01-2019/06/03 (invited conference presentation)
[13] X. Zhang, M. Li, H. Ding, and X. Yao. Data-driven tuning of feedforward controller structured with infinite impulse response filter via iterative learning control. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2019, 13(8): 1062-1070.
[14] W. Huang, K. Yang, Y. Zhu, X. Li, H. Mu, and M. Li. Data-driven rational feedforward tuning: With application to an ultraprecision wafer stage. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2020, 234(6): 748-758.
[15] T. Huang, K. Yang, C. Hu, Y. Zhu, and M. Li. Integrated robust tracking controller design for a developed precision planar motor with equivalent disturbances. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2016, 10(9):1009-1017.
[16] W. Huang, K. Yang, Y. Zhu, X. Li, H. Mu, and M. Li. Data-driven rational feedforward tuning: With application to an ultraprecision wafer stage. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2020, 234(6): 748-758.
[17] Q. Tang, F. Guo, T. Huang, K. Yang, Y. Zhu, and M. Li. Modal-Decomposition-Dependent State-Space Modeling and Modal Analysis of a Rigid-Flexible, Coupled, Multifreedom Motion System: Theory and Experiment. Shock and Vibration, 2020: 8859222.
[18] D. Yu, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, C. Hu, and M. Li. A time-varying Q-filter design for iterative learning control with application to an ultra-precision dual-stage actuated wafer stage. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2014, 228(9):658-667.
[19] M. Li, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, C. Hu, and H. Mu. A Variable-Gain Discrete Sliding Mode Control Strategy with PID-Type Sliding Surface for an Ultra-Precision Wafer Stage. Proceedings of the ASME 2016 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, Phoenix, USA, 2016: V04BT05A037.
[20] M. Li, K. Yang, Y. Zhu, and C. Hu. Optimal zero phase error tracking feedforward control for an ultra-precision dual-stage actuated wafer stage. Proceedings of ASPE 2014 Annual Meeting, Boston, USA, 2014: 226-231.
[21] X. Zhang, M. Li, H. Ding. Adaptive iterative learning control of fluidic muscle driven parallel manipulators for force control with sliding mode technique. Proceedings of the ASME 2020 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, Portland, USA, 2020.
[22] D. Yu, Y. Zhu, K. Yang, C. Hu, and M. Li. Combined nonlinear feedback and cascaded iterative learning control for an ultra-precision dual-stage actuated wafer stage. Proceedings of ASPE 2014 Annual Meeting, Boston, USA, 2014: 264-268.
Invention Patents:
[1] Zhu Yu, Zhang Ming, Li Min, et al. Three-degree-of-freedom displacement measurement method for moving coil planar motor: China, CN103292706B
[2] Zhu Yu, Yang Kaiming, Li Min, et al. A three-degree-of-freedom displacement measurement method for moving coil planar motor: China, CN103292707B
[3] Zhu Yu, Cheng Rong, Li Min, et al. An absolute grating signal processing method: China, CN103560780B
[4] Hu Chixiong, Zhu Yu, Wang Ze, Li Min, et al. A neural network adaptive trajectory tracking control method for permanent magnet synchronous linear motor: China, ZL 201610438862.1